What is “3D Printer”?
3D printer is a device that creates three-dimensional objects by stacking materials like resin or metal, based on digital 3D data. Unlike traditional printers that deal with 2D data, these bad boys let you freely craft shapes in three dimensions.

3D printing is a groundbreaking technology that manufactures objects layer by layer from a digital 3D model. It’s paving the way in fields like design, medicine, education, and manufacturing, offering faster, more cost-effective, and flexible production compared to traditional methods.
Types of 3D Printers
There’s a whole world of 3D printers out there, each with its own specialty. Some of the heavy hitters include:
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
FDM is the go-to for user-friendliness in 3D printing. It works by melting thermoplastic filament and laying it down layer by layer to shape an object. Great for prototypes or just tinkering around.
Stereolithography
This technique uses light to harden liquid resin into highly accurate and smooth-surfaced objects. It’s perfect when you need to nail those intricate details, like in jewelry or dental work.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
SLS uses lasers to sinter powdered material, layer by layer, creating objects without needing support structures. It’s a hit for complex geometries, widely used in engineering and aerospace.
Practical Uses of 3D Printers
With advancements in 3D printer performance and materials, these machines are revolutionizing manufacturing processes. Here’s what they can do:
Prototyping

In the design and development stage, 3D printers can whip up prototypes without molds, quickly and cost-effectively. This slashes development time, speeding up the journey to market.
Design Verification

At the planning stage, 3D-printed models can effectively share the final product’s vision, offering a more compelling presentation than traditional specs or illustrations.
Molds and Tooling

Traditionally, creating molds for processes like injection molding was both time-consuming and pricey. 3D printing offers a faster, cheaper alternative, especially beneficial during the prototyping phase.
Custom Tools and Jigs
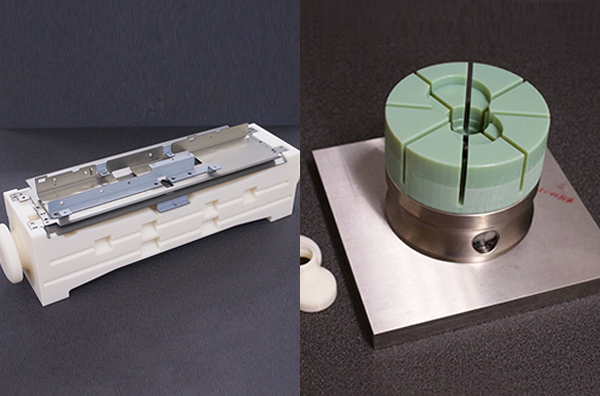
As products diversify, so does the need for specialized tools and jigs. 3D printers can rapidly produce these custom solutions, enhancing productivity.
Construction and Architectural Models
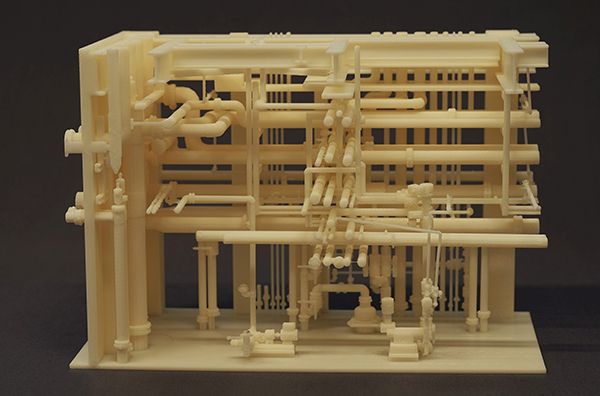
3D printers play a crucial role in architecture, allowing for the quick creation of detailed models. This not only aids client presentations but also facilitates internal reviews and method planning.
Final Products

Directly producing final products like custom orders, small batches, or replacement parts is a breeze with 3D printing. This eliminates the need for traditional mold-making, cutting costs and reducing lead times.
Advantages of 3D Printers
3D printers offer several advantages:
- Quick Turnaround: Significantly faster than traditional prototyping methods.
- Cost-Effective: More affordable than conventional approaches.
- Complex Shapes: Capable of creating intricate designs.
- Design Freedom: High design flexibility.
Disadvantages of 3D Printers
However, there are some drawbacks:
- Accuracy: Might not match traditional manufacturing methods.
- Material Limitations: Restricted material options.
- Cost: High-performance models can be pricey.
How to Choose a 3D Printer?
When selecting a 3D printer, consider the following:
- Purpose: What you’ll be using the 3D printer for.
- Budget: How much you’re willing to spend.
- Precision: The level of detail and accuracy you need.
- Printing Speed: How fast you need the printer to produce models.
- Material: The type of materials you want to use.
Choosing a 3D printer involves carefully evaluating your budget, required precision, print size, and the types of materials you plan to use. It’s also important to consider potential future upgrades.
The Future of 3D Printing
The outlook for 3D printing technology is broad and promising, with expected breakthroughs and progress in various aspects. Here are some potential developments:
Technological Advancements and Increased Precision
As 3D printing technology continues to evolve, we can expect improvements in print precision and speed. This will allow for the creation of products with finer, more complex designs that meet stricter industrial standards and requirements.
Material Innovation
A wider variety of printing materials will become available, including new alloys, advanced plastics, and biomaterials. These new materials will expand the application fields of 3D printing, playing significant roles in areas such as medical implants and aerospace components.
Cost Reduction
As the technology matures and production scales up, the costs of 3D printing equipment and materials are expected to decrease further. This will make 3D printing more accessible, offering more creative and innovative opportunities for small and medium-sized enterprises and individual users.
Expansion of Application Fields
3D printing will extend beyond prototype production and small-batch manufacturing to be used in large-scale production, construction, food manufacturing, and other new areas. Particularly in custom medical treatments and bioprinting, 3D printing technology is expected to enable the printing of personalized medicine, human tissues, and organs.
Sustainability
With an increasing focus on environmental consciousness, 3D printing will pay more attention to sustainability, including the use of recyclable materials, reducing waste in production processes, and lowering energy consumption.
Digitalization and Automation
The 3D printing process will become more digitalized and automated. By integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, 3D printing will achieve more efficient design optimization, production process management, and quality control.
Customization and Personalization
As consumer demand for personalized products grows, 3D printing will play a larger role in customized production. From personalized jewelry and clothing to custom medical devices and home goods, 3D printing technology will offer unprecedented personalized options to users.
Overall, the future of 3D printing technology will be an era of innovation, diverse materials, broad application fields, and sustainable development. With continuous technological advancements and cost reductions, 3D printing is poised to revolutionize traditional manufacturing, bringing more innovation and convenience to human society.
Efficient and Accurate Real-Time Translation Tool for Learning Foreign Cultures – Felo Translator

What is Felo Translator?
Felo Translator is an AI simultaneous interpretation app equipped with GPT-4 engine and RRT technology. It can quickly and accurately translate voice in more than 15 foreign languages (including English, Spanish, French, German, Russian, Chinese, Arabic, Japanese, etc.). It supports downloading original and translated text, helping you learn authentic expressions and pronunciation. ChatGPT, the large language model, accurately conveys the emotions, expressions, and dramatic effects of the play, enabling the audience to fully understand and enjoy the excitement brought by different language cultures.
How can Felo Translator assist simultaneous interpreters?
Felo Translator can assist beginners in simultaneous interpretation by solving the problem of falling behind in note-taking and ensuring more accurate translation of professional vocabulary.
Simultaneous interpretation is a complex and highly technical job that requires interpreters to have solid language skills, rich professional knowledge, and a good spirit of teamwork. Only by continuously learning and improving their translation abilities can they be competent in this important translation task and contribute to the smooth progress of international communication.
iOS Download | Android Download
